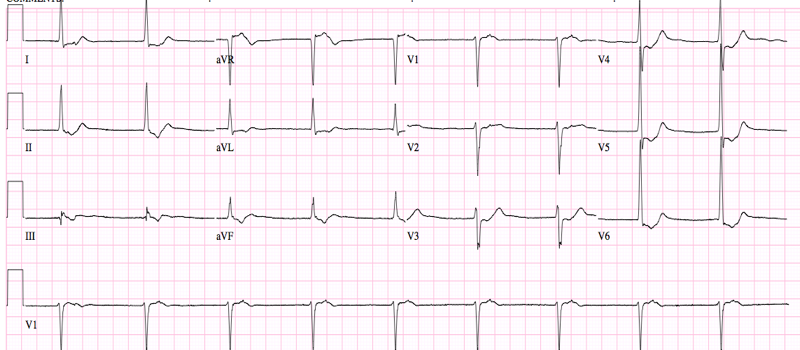
In a junctional rhythm, the sinus node fails to fire. Thus, you will not see sinus P waves (P waves from the sinus node will be upright in leads II, III, AVF, and negative in AVR). If the sinus node is not firing, then somthing must take over then to provide the electrical impetus for the the heart to beat. Often times, this will be the AV Node and it produces a junctional rhythm.
A juntional rhythm will have a rate of between 40-60 bpm. The QRS complexes will usually be narrow, and regular. On occasion, you may see retrograde P waves - that is, P waves that are the result not of the sinus node, but rather the impulse from the junction will travel backwards into the atrium and inscribe characteristic P waves that will be negative in the inferior leads (II, III, AVF).
ECG Criteria
1. Rate between 40-60 bpm
2. Narrow complex QRS (generally)
3. You may see retrograde P waves